Laboratory of Atomic and Nuclear Physics
The Laboratory of Atomic and Nuclear Physics was founded in 1969. It is hosted on the 1 st floor (East) and on the Basement (West) of the Faculty of Sciences building.
The members of the Laboratory pursue research in Nuclear Physics, Elementary Particle Physics (also known as High Energy Physics), Astroparticle Physics, and their applications. Their research topics cover the following areas:
- Experimental Nuclear Physics
- Experimental Elementary Particle Physics
- Experimental Astroparticle Physics
- Positronium Physics
- Dosimetry of Ionizing Radiation and Applications
- Development of detectors with applications in Nuclear and Astroparticle Physics
- Applications of Nuclear Physics – Physics of Radiation and of Isotopes
- Nuclear Physics Radiation – Applications in Energy, Medicine and the Environment
In a thematic perspective, the research in the Laboratory focuses on the following:
- Development of apparatus and methods for the detection of radiation
- Statistical techniques for analysis of data from experiments in accelerators at CERN, nuclear reactors, cosmic radiation, and environmental radiation.
- Measurements of interaction cross sections in reactions with nuclei, neutrons, protons, neutrinos, charged leptons and gauge bosons, as well as measurements of parameters of the Standard Model and search for New Physics,
- Dosimetry and radiation Physics, with applications in medicine and in radiometric dating, as well as in the handling of extraodinary incidents, like in radiological and nuclear accidents.
DIRECTOR
Stylianos StoulosMEMBERS
RESEARCH ACTIVITY
 Production of low and high energy neutron beams, from proton accelerator. Study of the cross sections of (n,γ), (n,α), (n,p) and (n, fission) interactions. Dose measurements from nutrons and γ-radiation.
Production of low and high energy neutron beams, from proton accelerator. Study of the cross sections of (n,γ), (n,α), (n,p) and (n, fission) interactions. Dose measurements from nutrons and γ-radiation.
RESEARCHERS

CAST experiment (CERN Axion Solar Telescope) is searching for the existence of solar axions. It utilizes a superconducting magnet, 10 m long and with a 9 Tesla magnetic field. Solar axions passing through the magnetic field is possible to be transformed into photons which could be detected by proper photon detectors. CAST has already improved the experimental limits by a factor of 10 and derived a limit better than the one resulting from astrophysical considerations. CAST will continue measuring up to the year 2010.
RESEARCHERS

Environmental Radioactivity: Atmospheric, Aquatic and Marine, Terrestrial. NORM: Naturally occurring radioactive materials: Uranium-238, Radium-226, Thorium-232, Potassium-40. Radon: Indoors, Outdoors, in Dwellings, in Caves. Radon: A precursor in earthquake prediction studies. Radioactive Aerosols. Radioactivity of Cosmic-ray origin: Beryllium-7, Sodium-22, Sulphur-35, Phosphorus-32, Phosphorus-33 Radioactivity in Karstic fields and Natural springs. TENORM: Technologically enhanced occurring radioactive materials. Radioactive fallout from nuclear reactor accidents: The case of Chernobyl accident. Radioactivity associated with the operation of Coal-fired power plants (CPP) Radioactivity associated with the operation of Phosphate ore processing plants (Phosphate Industries). Radioactivity of building materials. Radioecology: Radio-bio-indicators.
RESEARCHERS

The experiments concern to Nuclear Waste Transmutation of 237Np, 239Pu, 129I, 241Am, by using spallation sources of different design. Spectral measurements as well as spatial neutron and proton distributions at the source surface are performed in order to study the more efficient set up for transmutation. The experiments take place at the High Energy Lab. in Dubna, Russia, in the frame of the collaboration with European and ex-Soviet Union groups.
RESEARCHERS
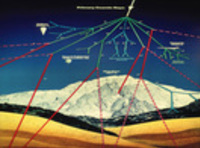
The interaction of primary cosmic ray particles with the atmosphere generates a variety of secondary particles (muons, gammas, neutrons, neutrinos...) some of which reach the surface of the Earth and they can be measured by ground based detectors. The interaction of very high energy cosmic rays with the atmosphere generates Extensive Atmospheric Showers (EAS) of secondaries. The study of EAS is on the research front and it is performed by a world-wide network of cosmic ray detectors.
RESEARCHERS

The High Energy Physics group of the AUTH which participates in the ATLAS experiment at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN has been constructed and tested part of the ATLAS muon spectrometer. The group has developed the methodology for detector construction in laboratorial installations of international specifications and allocates the essential experimental setup and software for the control of operation of detectors with comic rays. It also developed a test node of GRID technology for the analysis, distribution and storage of data. The group is developing data analysis methods and the essential software for the study of interactions of elementary particles in the ATLAS experiment.
